线程池¶
服务器基本框架¶
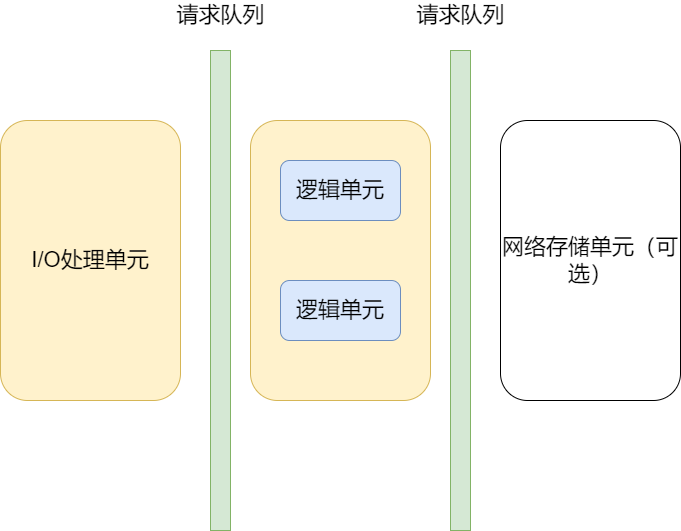
- I/O处理单元:处理客户端连接,读写网络数据
- 逻辑单元:处理逻辑业务
- 网络存储单元:本地数据和文件
I/O模型¶
同步IO¶
内核向用户进程通知的是就绪事件
* 阻塞IO:必须等待此函数返回才继续执行以下代码
* 非阻塞IO:每隔一段时间就去检测IO事件是否就绪;总是立即返回,在检测不到事件时立即返回后可以去做其他事情,如accept、send、recv等函数在设置成非阻塞之后,errno通常被设置为eagain
* 信号驱动IO:设置一个信号处理函数,程序没有阻塞阶段,IO事件就绪,收到SIGIO信号,处理事件(信号触发读写事件,用户程序执行读写操作)
* IO复用:select/poll函数实现IO复用;本身阻塞;但可以同时阻塞多个IO事件,可以同时对多个读事件、写事件遍历并操作
异步IO¶
内核向用户进程通知的是完成事件
linux中,可以调用aio_read函数告诉内核描述字缓冲区指针和缓冲区的大小、文件偏移及通知的方式,然后立即返回,当内核将数据拷贝到缓冲区后,再通知应用程序
事件处理模式¶
Reactor¶
要求主线程(I/O处理单元)只负责监听文件描述符上是否有事件发生,如果有则将该事件通知工作线程(逻辑单元)
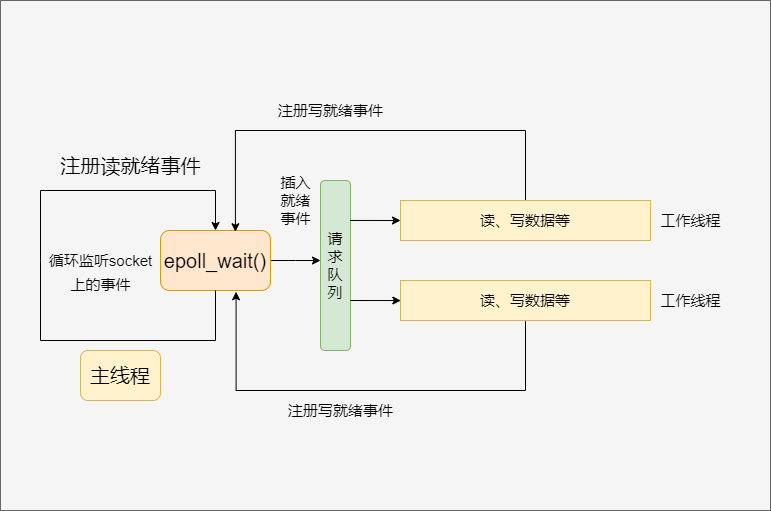
Proactor¶
将所有的I/O操作都交由主线程和内核来处理,工作线程负责处理业务逻辑
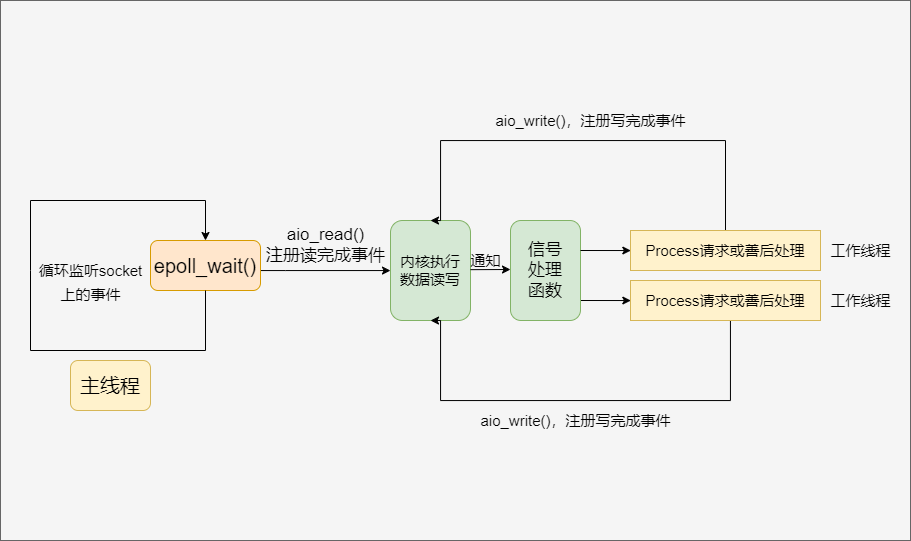
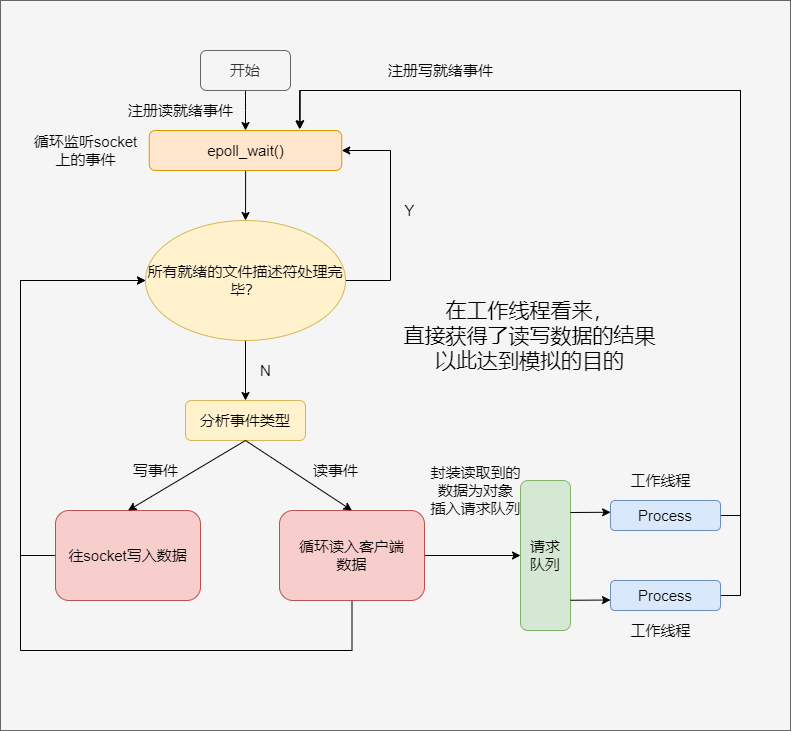
模拟Proactor¶
使用同步I/O模拟Proactor模式:
半同步/半异步并发模式¶
- 同步:程序完全按照代码执行顺序执行
- 异步:程序执行需要由系统事件驱动(中断、信号等)
同步线程处理客户逻辑(逻辑单元),异步线程用于处理I/O事件(I/O处理单元),异步线程监听到客户请求后,将其封装成对象插入请求队列中,请求队列通知处于同步模式的工作线程读取处理对象
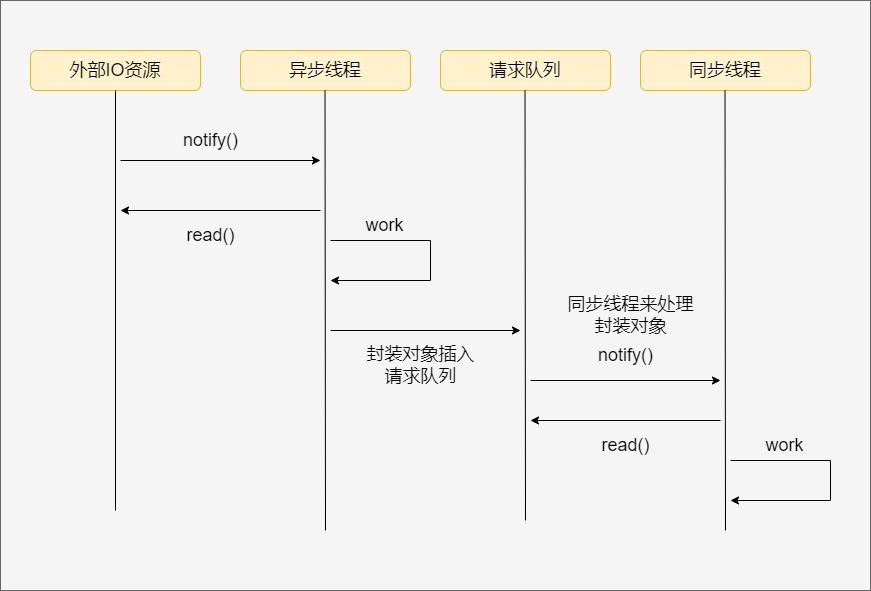
半同步/半反应堆并发模式¶
半同步/半异步模式的变体
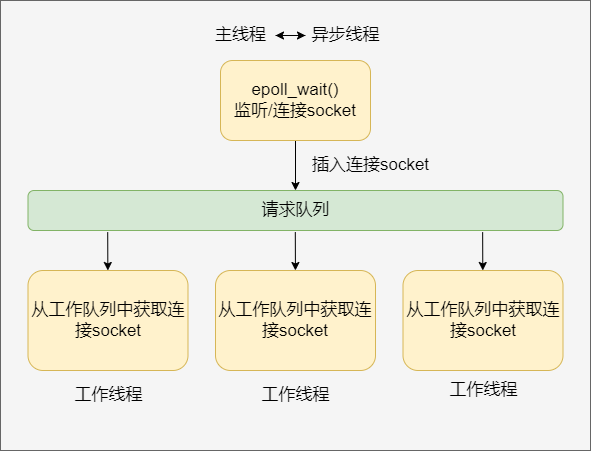
线程池特点¶
- 空间换时间
- 池:一组资源的集合,在服务器启动之前就已经初始化完毕(静态资源)
- 如果需要,从池中取得资源;不使用时将资源放回池中
- 描述:将线程池封装成一个类;构造函数用于初始化线程池;析构函数用于销毁线程池;
- 成员
- 记录线程池中线程的数量
- 请求队列,用于存放请求
- 记录请求队列中允许的最大请求数
- 维护线程池的指针
- 请求队列的互斥锁,用于线程同步中保证放取操作的原子性
- 请求队列的信号量,用于线程同步中允许同时工作的线程数量
- 事件处理模式,用于表示事件是Proactor还是Reactor
- 数据库连接池(还未涉及)
- 成员函数
- 将请求放入请求队列的操作函数
- 工作函数和线程处理函数,用于取出请求,唤醒工作线程以应对不同模式下对请求的处理
- 成员
pthread_create注意¶
pthread_create函数
第三个参数:函数指针,指向处理线程函数的地址;在类中要求为静态函数,因为该参数要求传入的函数指针指向的函数的参数为#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t* thread_id, const pthread_attr_t* attr, void* (*function)(void*), void* arg);
void*,如果是类成员函数(非static),则会默认传入一个this指针,这与函数要求相悖线程池实现¶
- 设计模式:半同步/半反应堆并发模式
- 反应堆:Proactor模式(事件处理模式,同步I/O模拟Proactor)
threadpool.h由于数据库部分暂未实现,所以暂时不关注#ifndef THREADPOOL_H #define THREADPOOL_H #include <list> #include <cstdio> #include <exception> #include <pthread.h> #include "../lock/locker.h" #include "../CGImysql/sql_connection_pool.h" //数据库连接使用,这里暂时还用不上 template<typename T> class threadpool { public: threadpool(int actor_model/*Proactor*/, connection_pool* connPool/*连接池*/, int thread_num = 8/*线程池中的线程数量*/, int max_requests = 1000/*请求队列中最多允许的、等待处理的请求数量*/); ~threadpool(); //向请求队列中插入请求: 写 1;读 0 bool append(T* request, int state); //向请求队列中插入请求 bool append(T* request); private: //工作函数(转交run函数处理线程),设置为static static void* worker(void* arg); //线程处理函数 void run(); private: int m_thread_num; //线程池线程数量 int m_max_requests; //请求队列中允许的最大请求数 pthread_t* m_threads; //线程池 std::list<T*> m_workqueue; //请求队列 locker m_queuelocker; //队列的互斥锁 sem m_queuestate; //队列的信号量 connection_pool* m_connPool; //数据库连接池 int m_actor_model; //事件处理模式 }; //初始化线程池中的线程 template<typename T> threadpool<T>::threadpool(int actor_model, connection_pool* connPoll, int thread_num, int max_requests): m_actor_model(actor_model), m_thread_num(thread_num), m_max_requests(max_requests), m_threads(NULL), m_connPool(connPoll) { if(thread_num <= 0 || max_requests <=0) { throw std::exception(); } m_threads = new pthread_t[m_thread_num]; if(!m_threads) { throw std::exception(); } for(int i=0; i<thread_num; i++) { if(pthread_create(m_threads+i, NULL, worker, this) != 0) { delete[] m_threads; throw std::exception(); } //使每个线程分离:退出线程时资源自动回收 if(pthread_detach(m_thread[i])) { delete[] m_threads; throw std::exception(); } } } //工作线程 template<typename T> void* threadpool<T>::worker(void* arg) { threadpool* pool = (threadpool*)arg; //将void*参数强制转换为threadpool*,以便调用线程处理函数run pool->run(); return pool; } //线程处理函数 template<typename T> void threadpool<T>::run() { while(true) { m_queuestate.wait(); //等待信号量通知 //此时有空闲的工作线程,所以请求队列中取出请求 //由于处于竞争状态,所以需要加锁 m_queuelocker.lock(); if(m_workqueue.empty()) continue; //请求对垒为空,继续等待(处理虚假唤醒) T* request = m_workqueue.front(); m_workqueue.pop_front(); m_queuelocker.unlock(); if(!request) continue; if(1 == m_actor_model) //Reactor { if(0 == request->m_state) //读事件 { //读事件处理逻辑 }else { //写事件 //写事件处理逻辑 } } else { //默认0:Proactor // Proactor处理逻辑 } } } template<typename T> threadpool<T>::~threadpool() { delete[] m_threads; } //添加请求 template<typename T> bool threadpool<T>::append(T* request, int state) { m_queuelocker.lock(); if(m_workqueue.size() >= m_max_requests) { m_queuelocker.unlock(); return false; } request->m_state = state; m_workqueue.push_back(request); m_queuelocker.unlock(); m_queuestate.post(); //信号量+1,说明此时有一个工作线程 return true; } //添加请求:无状态版本 template<typename T> bool threadpool<T>::append_p(T* request) { m_queuelocker.lock(); if(m_workqueue.size() >= m_max_requests) { m_queuelocker.unlock(); return false; } m_workqueue.push_back(request); m_queuelocker.unlock(); m_queuestate.post(); return true; } #endif