C++11 习STL有感--List篇(一)¶
最近在项目上经常遇到一些需要重复使用的变量,并且这些变量可能会因为项目迁移或者复用等原因具有很强的宏概括性,也即在不同的项目上可能仅仅是名称不一但对于此类变量的使用方式和逻辑确实一样的等,所以经常使用配置文件的方式保存这些变量,使用加载类将配置文件的信息加载进一个我们传入的容器,在项目源代码上只需要使用该容器即可。那么了解各个容器就显得格外的重要,作为C/C++开发工程师来说,我们应该考虑不同容器或者适配器对于变量加载、保存使用、拷贝等有关于计算和内存开销等的大小。在此读下源码,对STL有进一步的了解。
list¶
list相关的继承类是封装在__detail命名空间中:
_list_node_base¶
list节点基类:
struct _List_node_base
{
_List_node_base* _M_next; //指向前一个节点基类的指针
_List_node_base* _M_prev; //指向后一个节点基类的指针
// 交换节点基类的函数,注意,_GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT ==> noexcept
static void
swap(_List_node_base& __x, _List_node_base& __y) _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT;
// 用于将从__first到__last之间的节点转移到另一个位置
void
_M_transfer(_List_node_base* const __first,
_List_node_base* const __last) _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT;
// 用于将链表节点反转
void
_M_reverse() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT;
// 用于将当前节点插入到指定位置之前
void
_M_hook(_List_node_base* const __position) _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT;
// 在链表中移除当前节点
void
_M_unhook() _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT;
};
在此简单说下成员函数的原理:
- swap:用于交换节点,可能的实现如下:
static void _List_node_base::swap(_list_node_base &__x, _list_node_base&__y) _GLIBCXX_USE_NOEXCEPT {
_list_node_base __x_pre = __x._M_prev;
_list_node_base __x_next = __x._M_next;
_list_node_base __y_pre = __y._M_prev;
_list_node_base __y_next = __y._M_next;
// 更新__x节点的前向和后向指针:指向原来__y节点的前向指针和后向指针
__x._M_prev = __y_pre;
__x->_M_next = __y_next;
__y_pre->_M_next = __x;
__y_next->_M_prev = __x;
// 更新__y节点的前向和后向指针:指向原来__x节点的前向指针和后向指针
__y._M_prev = __x_pre;
__y->_M_next = __x_next;
__x_pre->_M_next = __y;
__x_next->_M_prev = __y;
}
当然,可以不使用局部变量对__x和__y的前节点和后节点进行存储,可直接进行指向,但可能会让代码变得晦涩难懂。
- _M_transfer:
void _List_node_base::_M_transfer(_List_node_base* const __first,
_List_node_base* const __last) noexcept
{
if (__first != __last)
{
// 将要转移的范围中的第一个节点的前指针指向 last 的前指针
__first->_M_prev->_M_next = __last;
// 将 last 的前指针指向要转移的范围中的第一个节点的前指针
__last->_M_prev->_M_next = this;
// 将要转移的范围中的最后一个节点的后指针指向 this
__last->_M_prev = prev;
// 将要转移的范围中的第一个节点的前指针指向 this
__first->_M_prev = this;
// 将 this 的前指针指向要转移的范围中的最后一个节点的后指针
prev = __last->_M_prev;
}
}
- _M_reverse:
void _List_node_base::_M_reverse() noexcept
{
// 如果链表为空或只有一个节点,则无需反转
if (this->next == this || this->next->next == this)
return;
_List_node_base* current = this->_M_next;
_List_node_base* next_node = nullptr;
this->_M_prev = current; // 更新头节点的 prev 指针
// 反转链表
while (current != this)
{
next_node = current->_M_next;
// 交换节点的前向指针和后向指针
current->_M_next = this;
current->_M_prev = next_node;
current = next_node;
}
this->_M_next = current; // 更新头节点的 next 指针
}
- _M_hook:
void _List_node_base::_M_hook(_List_node_base* const __position) noexcept
{
// 更新当前节点的前向指针和后向指针
this->_M_prev = __position->_M_prev;
this->_M_next = __position;
// 更新相邻节点的指针
__position->_M_prev->_M_next = this;
__position->_M_prev = this;
}
- _M_unhook:
void _List_node_base::_M_unhook() noexcept
{
// 更新相邻节点的指针
this->_M_prev->_M_next = this->_M_next;
this->_M_next->_M_prev = this->_M_prev;
// 将当前节点的前向指针和后向指针设置为nullptr
this->_M_prev this->_M_next = nullptr;
}
_list_node_header¶
list头节点:
/// The %list node header.
struct _List_node_header : public _List_node_base
{
#if _GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI
std::size_t _M_size; //C++11多了个表示大小的size
#endif
_List_node_header() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ _M_init(); }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L //C++11及以上标准多个移动构造
_List_node_header(_List_node_header&& __x) noexcept
: _List_node_base{ __x._M_next, __x._M_prev }
# if _GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI
, _M_size(__x._M_size)
# endif
{
//传进来的链表为空,那么初始化头节点链表为空
if (__x._M_base()->_M_next == __x._M_base())
this->_M_next = this->_M_prev = this;
else
{ //确保自身头节点链表的连接性,初始化__x头节点(由于前面初始化列表已经将__x的base进行初始化了,
// 所以相当于将__x移动到当前头节点链表中)
this->_M_next->_M_prev = this->_M_prev->_M_next = this->_M_base();
__x._M_init();
}
}
void
_M_move_nodes(_List_node_header&& __x) //移动该头节点
{
_List_node_base* const __xnode = __x._M_base();
if (__xnode->_M_next == __xnode) //链表为空,重新初始化
_M_init();
else
{ //将当前的头节点移动为传入的头节点
_List_node_base* const __node = this->_M_base();
__node->_M_next = __xnode->_M_next;
__node->_M_prev = __xnode->_M_prev;
__node->_M_next->_M_prev = __node->_M_prev->_M_next = __node;
# if _GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI
_M_size = __x._M_size;
# endif
__x._M_init();
}
}
#endif
void
_M_init() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT //初始化头节点
{
this->_M_next = this->_M_prev = this;
#if _GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI
this->_M_size = 0;
#endif
}
private:
_List_node_base* _M_base() { return this; }
};
_list_node¶
list中的节点:真正使用list的时候存储元素的节点
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_node : public __detail::_List_node_base
{
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
__gnu_cxx::__aligned_membuf<_Tp> _M_storage;
_Tp* _M_valptr() { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
_Tp const* _M_valptr() const { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
#else
_Tp _M_data;
_Tp* _M_valptr() { return std::__addressof(_M_data); }
_Tp const* _M_valptr() const { return std::__addressof(_M_data); }
#endif
};
分为C++11之前的实现和之后的实现:
C++11标准之前的实现:模板类型成员,成员函数的实现是直接返回数据成员的地址;
C++11标准之后的实现:
__gnu_cxx::__aligned_membuf<_Tp> _M_storage
使用内存对齐的方式初始化:__gnu_cxx::__aligned_membuf<_Tp>是一个模板类,用于对齐内存的分配。它确保_M_storage的内存分配是按照所需的类型进行对齐的。对齐内存可以提高访问和操作内存的性能,因为它允许CPU以更高效的方式读取和写入数据
_M_storage和_M_valptr:
template<typename _Tp>
struct __aligned_membuf
{
struct _Tp2 { _Tp _M_t; };
alignas(__alignof__(_Tp2::_M_t)) unsigned char _M_storage[sizeof(_Tp)];
};
对于初始化类型的内存进行对齐,使用_M_storage字节数组进行管理
_Tp* _M_valptr() { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
_Tp const* _M_valptr() const { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); }
_M_ptr()在aligned_buffer.h中实现如下:
template<typename _Tp>
struct __aligned_membuf
{
...
const void*
_M_addr() const noexcept
{ return static_cast<const void*>(&_M_storage); }
_Tp*
_M_ptr() noexcept
{ return static_cast<_Tp*>(_M_addr()); }
};
其实就是返回_M_storage的地址
- C++11之后的版本较之前的版本有什么好处呢?
在之前的版本中,std::list使用一个指针指向一个动态分配的节点,每个节点包含两个指针用于指向前一个和后一个节点。然而,这种实现方式可能导致内存碎片化,因为节点可以在堆中不连续的位置分配。此外,由于缺乏内存对齐,可能会导致性能下降;通过使用__aligned_membuf<_Tp> _M_storage,C++11中的std::list能够提高性能和空间利用率。它减少了内存碎片化,提供了连续的内存区域,并对齐内存以获得更好的访问性能。这些优化让std::list在实际使用中更加高效和可靠
_list_iterator¶
list迭代器:用于list节点的遍历、获取元素进行相关操作等
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_iterator
{
typedef _List_iterator<_Tp> _Self;
typedef _List_node<_Tp> _Node;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // 指针之间的距离
typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; //迭代器类型:双向迭代器
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
_List_iterator() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node() { }
explicit //显示构造:只允许传入类型为_list_node_base的节点进行构造
_List_iterator(__detail::_List_node_base* __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node(__x) { }
_Self
_M_const_cast() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *this; }
// Must downcast from _List_node_base to _List_node to get to value.
reference
operator*() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *static_cast<_Node*>(_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
pointer
operator->() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return static_cast<_Node*>(_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
_Self&
operator++() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_M_node = _M_node->_M_next;
return *this;
}
_Self
operator++(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT //后++
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _M_node->_M_next;
return __tmp;
}
_Self&
operator--() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_M_node = _M_node->_M_prev;
return *this;
}
_Self
operator--(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _M_node->_M_prev;
return __tmp;
}
friend bool
operator==(const _Self& __x, const _Self& __y) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return __x._M_node == __y._M_node; }
#if __cpp_impl_three_way_comparison < 201907L //是否支持三路比较
friend bool
operator!=(const _Self& __x, const _Self& __y) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return __x._M_node != __y._M_node; }
#endif
// The only member points to the %list element.
__detail::_List_node_base* _M_node;
};
-
实现指针行为
-
为什么
_list_iterator继承的是_list_node_base,而不是_list_node呢?
继承_list_node_base的原因:只有前向指针和后向指针,对于迭代器行为更加纯粹,不包含实际元素,也是为了实现迭代器失效规则;在list容器中,当对容器进行插入和删除操作时,已经获取到的指向容器元素的迭代器可能会失效。为了确保迭代器失效后仍然能够正确遍历容器,list_iterator需要保留一个指向实际节点的指针,而不是使用_list_node
- 小知识点
`__cpp_impl_three_way_comparison:__cpp_impl_three_way_comparison是一个宏,用于指示C++标准库是否支持三路比较(three-way comparison)的实现。三路比较是C++20引入的一个新特性,它允许用户定义自己的对象之间的比较操作符(例如==、<、>等),并且可以返回三个不同的结果:小于、等于或大于。在之前的C++标准中,比较操作符只能返回布尔值。__cpp_impl_three_way_comparison的值代表一个实现该特性的C++编译器的版本。如果该宏被定义并且其值大于等于201711,则表示编译器实现了三路比较。需要注意的是,__cpp_impl_three_way_comparison是一个编译器特定的宏,并不是C++标准中定义的。因此,其行为和值的具体含义可能会因不同的编译器而有所不同。建议在编写使用该宏的代码时,查阅相关编译器的文档以了解其具体行为。
_list_const_iterator¶
同上,只是多了const属性:
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_const_iterator
{
typedef _List_const_iterator<_Tp> _Self;
typedef const _List_node<_Tp> _Node;
typedef _List_iterator<_Tp> iterator;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef const _Tp* pointer;
typedef const _Tp& reference;
_List_const_iterator() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node() { }
explicit
_List_const_iterator(const __detail::_List_node_base* __x)
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node(__x) { }
_List_const_iterator(const iterator& __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node(__x._M_node) { }
iterator
_M_const_cast() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return iterator(const_cast<__detail::_List_node_base*>(_M_node)); }
// Must downcast from List_node_base to _List_node to get to value.
reference
operator*() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *static_cast<_Node*>(_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
pointer
operator->() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return static_cast<_Node*>(_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
_Self&
operator++() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_M_node = _M_node->_M_next;
return *this;
}
_Self
operator++(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _M_node->_M_next;
return __tmp;
}
_Self&
operator--() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_M_node = _M_node->_M_prev;
return *this;
}
_Self
operator--(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _M_node->_M_prev;
return __tmp;
}
friend bool
operator==(const _Self& __x, const _Self& __y) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return __x._M_node == __y._M_node; }
#if __cpp_impl_three_way_comparison < 201907L
friend bool
operator!=(const _Self& __x, const _Self& __y) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return __x._M_node != __y._M_node; }
#endif
// The only member points to the %list element.
const __detail::_List_node_base* _M_node;
};
_list_base¶
上述讲解的是关于list节点的相关类型,而list需要由一个类用于组织或者说管理这些节点。在STL中,_list_base是一个辅助类,用于管理双向链表的头部和尾部节点以及链表的大小。它是作为std::list的基类存在的,并不是由开发者直接使用的:
emplate<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
class _List_base
{
protected:
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type; // 1
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type> _Tp_alloc_traits;
typedef typename _Tp_alloc_traits::template
rebind<_List_node<_Tp> >::other _Node_alloc_type; // 2
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Node_alloc_type> _Node_alloc_traits;
#if !_GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION
static size_t
_S_distance(const __detail::_List_node_base* __first,
const __detail::_List_node_base* __last)
{ //_List_base中可以计算两个基节点之间的距离
size_t __n = 0;
while (__first != __last)
{
__first = __first->_M_next;
++__n;
}
return __n;
}
#endif
struct _List_impl
: public _Node_alloc_type
{
__detail::_List_node_header _M_node;
_List_impl() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT_IF(
is_nothrow_default_constructible<_Node_alloc_type>::value)
: _Node_alloc_type()
{ }
_List_impl(const _Node_alloc_type& __a) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _Node_alloc_type(__a)
{ } // 3
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
_List_impl(_List_impl&&) = default;
_List_impl(_Node_alloc_type&& __a, _List_impl&& __x)
: _Node_alloc_type(std::move(__a)), _M_node(std::move(__x._M_node))
{ } // 本身需要实现右指引用传参的构造函数或者保证不抛异常
_List_impl(_Node_alloc_type&& __a) noexcept // 如上说明
: _Node_alloc_type(std::move(__a))
{ }
#endif
};
_List_impl _M_impl; // 实现链表
#if _GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI
size_t _M_get_size() const { return _M_impl._M_node._M_size; }
void _M_set_size(size_t __n) { _M_impl._M_node._M_size = __n; }
void _M_inc_size(size_t __n) { _M_impl._M_node._M_size += __n; } //increase
void _M_dec_size(size_t __n) { _M_impl._M_node._M_size -= __n; } //decrease
# if !_GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION
size_t
_M_distance(const __detail::_List_node_base* __first,
const __detail::_List_node_base* __last) const
{ return _S_distance(__first, __last); }
// return the stored size
size_t _M_node_count() const { return _M_get_size(); }
# endif
#else
// dummy implementations used when the size is not stored
size_t _M_get_size() const { return 0; }
void _M_set_size(size_t) { }
void _M_inc_size(size_t) { }
void _M_dec_size(size_t) { }
# if !_GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION
size_t _M_distance(const void*, const void*) const { return 0; }
// count the number of nodes
size_t _M_node_count() const
{
return _S_distance(_M_impl._M_node._M_next,
std::__addressof(_M_impl._M_node));
}
# endif
#endif
typename _Node_alloc_traits::pointer
_M_get_node()
{ return _Node_alloc_traits::allocate(_M_impl, 1); } // 4
void
_M_put_node(typename _Node_alloc_traits::pointer __p) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ _Node_alloc_traits::deallocate(_M_impl, __p, 1); }
public:
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
_Node_alloc_type&
_M_get_Node_allocator() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_impl; } //返回_list_impl类型,转化为_Node_alloc_type节点分配器类型,表示获取节点实现类类型(获取分配器类型)
const _Node_alloc_type&
_M_get_Node_allocator() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_impl; }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
_List_base() = default; //C++11标准及以上默认构造行为
#else
_List_base() { }
#endif
_List_base(const _Node_alloc_type& __a) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_impl(__a)
{ }
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
_List_base(_List_base&&) = default;
# if !_GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION
_List_base(_List_base&& __x, _Node_alloc_type&& __a)
: _M_impl(std::move(__a))
{
if (__x._M_get_Node_allocator() == _M_get_Node_allocator()) //分配器类型相等
_M_move_nodes(std::move(__x)); //则转移构造
// else caller must move individual elements.
}
# endif
// Used when allocator is_always_equal.
_List_base(_Node_alloc_type&& __a, _List_base&& __x)
: _M_impl(std::move(__a), std::move(__x._M_impl))
{ }
// Used when allocator !is_always_equal.
_List_base(_Node_alloc_type&& __a)
: _M_impl(std::move(__a))
{ } //对应_list_impl上述的构造函数
void
_M_move_nodes(_List_base&& __x)
{ _M_impl._M_node._M_move_nodes(std::move(__x._M_impl._M_node)); } //移动头节点
#endif
// This is what actually destroys the list.
~_List_base() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ _M_clear(); }
void
_M_clear() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT;
void
_M_init() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ this->_M_impl._M_node._M_init(); }
};
- 注释1和2处的rebind:
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type;这句代码是用来定义一个名为_Tp_alloc_type的类型别名,其类型是_Alloc模板参数所对应的分配器类型经过重新绑定(rebind)到_Tp类型的结果。__gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>是 GNU C++ 标准库中的一个辅助类型,在__gnu_cxx命名空间中定义。它提供了有关分配器类型的信息和转换;__alloc_traits::template rebind<_Tp>是一个模板成员函数,用于重新绑定分配器类型到指定的类型_Tp(rebind函数的目的是为了在使用不同的元素类型时重新创建相应的分配器类型);typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other表示通过rebind函数得到的重新绑定后的分配器类型的别名(other是 rebind 结果的别名);使用typedef关键字将typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other定义为_Tp_alloc_type,使得_Tp_alloc_type表示了_Alloc分配器类型经过重新绑定到_Tp类型的结果,它是_Alloc的一个别名。这样做的目的是方便在容器的内部使用分配器,确保将正确的分配器类型应用到相应的容器元素类型上。typedef typename _Tp_alloc_traits::template rebind<_List_node<_Tp> >::other _Node_alloc_type;同理可分析为根据分配器类型_Tp_alloc_traits对_list_node<Tp>重新绑定的结果,确保在分配和释放_List_node<_Tp>类型对象的内存时使用正确的分配器 - _GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION是什么? GNU C++ 标准库使用
_GLIBCXX_INLINE_VERSION宏来确定库的内部实现和某些特性的可用性。该宏的值与标准库的版本号相关,此版本该宏为0 - 注释3:这段代码定义了
_List_impl类的构造函数,并使用了_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT_IF来指明该构造函数在满足特定条件时不会抛出异常。is_nothrow_default_constructible是一个类型特性,用于检查指定类型是否具有无异常默认构造函数,value是一个静态成员常量,它的值表示该类型是否具有无异常默认构造函数。整个构造函数的目的是创建一个_List_impl类对象的实例,并使用默认构造函数来初始化_Node_alloc_type成员。同时,通过_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT_IF宏的条件,表示只有当_Node_alloc_type的默认构造函数不会抛出异常时,该构造函数才不会抛出异常 - 注释4:这段代码定义了一个名为
_M_get_node的成员函数,函数返回一个_Node_alloc_traits::pointer类型的指针,并使用_Node_alloc_traits::allocate()来分配内存。首先,_M_get_node函数的返回类型是_Node_alloc_traits::pointer。这是由_Node_alloc_traits类型定义的分配器类型的指针类型。_Node_alloc_traits是一个表示分配器特性的类型,它包含有关分配器类型的信息和转换。在函数体内,调用_Node_alloc_traits::allocate(_M_impl, 1)来分配内存。allocate()是分配器类型的一个成员函数,它被用来分配指定数量的内存块。_M_impl是_List_impl类的一个成员变量,它代表链表的实现。_M_impl是一个指向链表实现的指针。这个指针将传递给allocate()函数作为分配器的参数,以指示在哪里分配内存。1是要分配的内存块数量。在这里,我们只需要分配一个节点的内存。整个函数的目的是从给定的_Node_alloc_traits分配器类型中获取一个节点的内存块,并将其作为指针返回。这样,返回的指针可以用于存储链表中的节点的地址,从而实现链表的动态管理和存储。
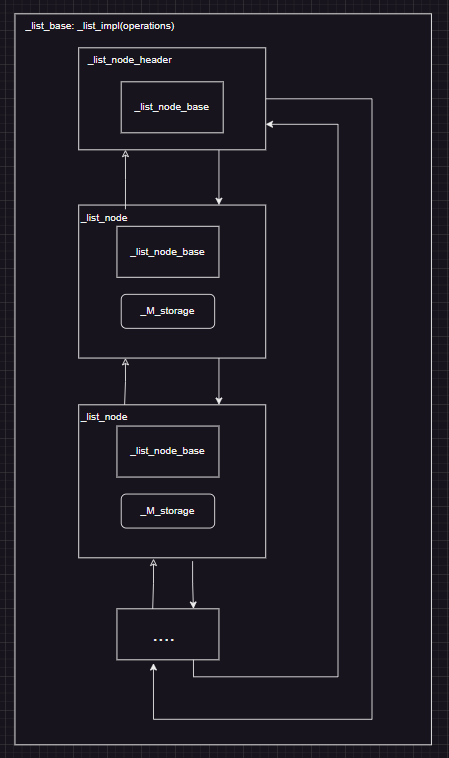
说到这,已经将stl中构成list的几个基本类说完了,在进入list类说明之前,先捋一下上述说的_list_node_base、_list_node_header、_list_node和_list_base的关系:
_list_node_base是list节点的基类,其职责很简单,就是提供节点的前向指针和后向指针,方便对指向各个节点之间的关系。
_list_node是基于list节点基类的基础上,存储节点元素(值)的节点。
_list_node_header是基于list节点基类的基础上,用于表示list的头节点,并提供list的大小。
_list_base是实现list的基础,提供了list的基础操作(加入节点,删除节点等),其中提供操作由类中的_list_impl类实现,并包含指向list的头节点。