one_thread_one_loop 思想¶
基于Reactor
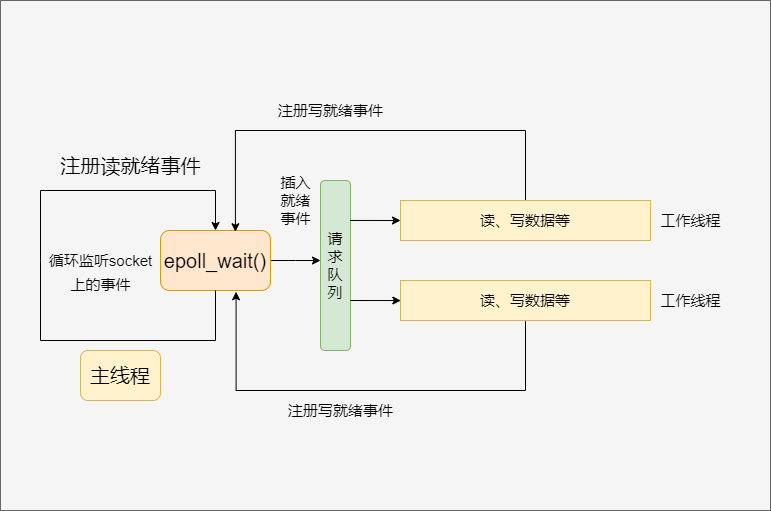
一个线程对应一个循环,即每个线程函数里有一个循环处理
void* thread_function(void*) {
//init
while(true) {
// 1: select/poll/epoll等待事件(分离读写事件)
epoll_poll_select();
// 2: 处理读写事件
handle_io_events();
// 3: other things...
handle_other_things();
}
}
对于步骤二:
以socket对象为例,如果是处理读事件,对于监听socket来说,读事件一般就是接受新的连接,除此之外,还可以accept()到新的连接之后对连接进行设置并绑定到IO复用上去;对于普通的socket,还可以调用recv或者read函数接收数据、解包、处理事务逻辑等。如果是处理写事件,一般就是发送数据
对于步骤三:
可以是上述步骤二提到的对于数据的处理等(业务分离)
基于Reactor¶
基于Reactor实现的是线程分工
主线程负责接收连接,并把接收到的连接交由子线程负责处理
- 主线程只负责接收连接,不处理IO事件
- 主线程接收到的连接派发给子线程(工作线程),派发策略可以是轮循
- 子线程(工作线程)在处理完IO事件之后,还可以进入
handle_other_things()处理其他事务
问题¶
epoll_poll_select()中,如果设置超时时间为0,则在监测不到事件时则这些工作线程会一直空转,白白浪费时间;如果设置了一定的超时时间,工作线程会挂起直到有事件发生epoll_poll_select()函数返回,则会导致步骤三handle_other_things()函数的任务无法及时执行
想要达到的效果:
没有IO事件的时候,工作线程直接挂起而不是等待,如果有其他任务要处理,则工作线程能立即处理
解决策略:
- 为
epoll_poll_select()函数设置一定的超时时间 - 对于
handle_other_things()函数实现特殊的唤醒机制
唤醒机制¶
不管epoll_fd上有没有事件,绑定一个wakeup_fd。
当需要handle_other_things()立刻执行时(有其他任务要做),则向wakeup_fd写入一个字节数据,让其变为可读,则epoll_poll_select()函数会立即返回,执行handle_io_events()之后执行handle_other_things()
唤醒机制实现¶
管道fd¶
- 创建一个管道
- 将管道的一端绑定到epollfd上
- 唤醒时,向管道的另一端写入数据
创建管道函数
eventfd¶
将生成的 eventfd() 函数返回的 eventfd 绑定到 epollfd上,需要唤醒时,向这个 eventfd 上写入数据
socketpair¶
一对相互连接的socket,每一段都可以读写数据,向其中一端写入数据,另一端读取数据
下述的sv[2]就是两个读写端,将调用socketpair()函数返回的sv绑定到epollfd,其中一个端口写入数据
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
//domain: must be AF_UNIX
int socketpair(int domain, int type, int protocol, int sv[2]);
程序举例¶
唤醒机制实现:
bool EventLoop::createWakeupfd()
{
#ifdef WIN32 //Windows平台下
wakeupFdListen_ = sockets::createOrDie();
wakeupFdSend_ = sockets::createOrDie();
//Windows上需要创建一对socket:socket_1和 socket_2
struct sockaddr_in bindaddr; //socket_1:绑定连接
bindaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
bindaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_LOOPBACK);
//将port设为0,然后进行bind,再接着通过getsockname来获取port,这可以满足获取随机端口的情况。
//原因:
//实现多个工作线程可能存在多个端口号,如果有新的线程调用bind函数绑定相同的端口号会导致调用失败
bindaddr.sin_port = 0;
sockets::setReuseAddr(wakeupFdListen_, true);
sockets::bindOrDie(wakeupFdListen_, bindaddr);
sockets::listenOrDie(wakeupFdListen_);
struct sockaddr_in serveraddr; //socket_2:监听接收的本端连接
int serveraddrlen = sizeof(serveraddr);
if (getsockname(wakeupFdListen_, (sockaddr*)& serveraddr, &serveraddrlen) < 0)
{
//让程序挂掉
LOGF("Unable to bind address info, EventLoop: 0x%x", this);
return false;
}
int useport = ntohs(serveraddr.sin_port);
LOGD("wakeup fd use port: %d", useport);
//serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
//serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
//serveraddr.sin_port = htons(INNER_WAKEUP_LISTEN_PORT);
if (::connect(wakeupFdSend_, (struct sockaddr*) & serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr)) < 0)
{
//让程序挂掉
LOGF("Unable to connect to wakeup peer, EventLoop: 0x%x", this);
return false;
}
struct sockaddr_in clientaddr; //对端的客户端连接
socklen_t clientaddrlen = sizeof(clientaddr);
wakeupFdRecv_ = ::accept(wakeupFdListen_, (struct sockaddr*) & clientaddr, &clientaddrlen);
if (wakeupFdRecv_ < 0)
{
//让程序挂掉
LOGF("Unable to accept wakeup peer, EventLoop: 0x%x", this);
return false;
}
sockets::setNonBlockAndCloseOnExec(wakeupFdSend_);
sockets::setNonBlockAndCloseOnExec(wakeupFdRecv_);
#else
//Linux上一个eventfd就够了,可以实现读写
wakeupFd_ = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);
if (wakeupFd_ < 0)
{
//让程序挂掉
LOGF("Unable to create wakeup eventfd, EventLoop: 0x%x", this);
return false;
}
#endif
return true;
}
唤醒函数实现:
bool EventLoop::wakeup()
{
//向一端socket写入一个字节数据,使其事件变为可读
uint64_t one = 1;
#ifdef WIN32
int32_t n = sockets::write(wakeupFdSend_, &one, sizeof(one));
#else
int32_t n = sockets::write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
#endif
if (n != sizeof one) //如果写入的数据出错,打印出错日志
{
#ifdef WIN32
DWORD error = WSAGetLastError();
LOGSYSE("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %d bytes instead of 8, fd: %d, error: %d", n, wakeupFdSend_, (int32_t)error);
#else
int error = errno;
LOGSYSE("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %d bytes instead of 8, fd: %d, error: %d, errorinfo: %s", n, wakeupFd_, error, strerror(error));
#endif
return false;
}
return true;
}
从唤醒的fd上及时读取掉这一个字节数据:(在唤醒fd之后调用)
才不会因为多次的调用而导致缓冲区占满或者溢出等错误
bool EventLoop::handleRead()
{
//及时读取
uint64_t one = 1;
#ifdef WIN32
int32_t n = sockets::read(wakeupFdRecv_, &one, sizeof(one));
#else
int32_t n = sockets::read(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
#endif
if (n != sizeof one)
{
#ifdef WIN32
DWORD error = WSAGetLastError();
LOGSYSE("EventLoop::wakeup() read %d bytes instead of 8, fd: %d, error: %d", n, wakeupFdRecv_, (int32_t)error);
#else
int error = errno;
LOGSYSE("EventLoop::wakeup() read %d bytes instead of 8, fd: %d, error: %d, errorinfo: %s", n, wakeupFd_, error, strerror(error));
#endif
return false;
}
return true;
}
handle_other_things¶
void EventLoop::handle_other_things()
{
std::vector<OtherThingFunctor> otherThingFunctors;
callingPendingFunctors_ = true;
{
//pendingOtherThingFunctors_是一个类成员变量
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
//减小锁的作用域(粒度):swap 使用了一个局部变量 otherThingFunctors 将成员变量 pendingOtherThingFunctors_ 的中的数据倒换进这个局部变量中
otherThingFunctors.swap(pendingOtherThingFunctors_);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < otherThingFunctors.size(); ++i)
{
otherThingFunctors[i](); //将任务封装成一个个任务对象,取出直接执行即可
}
callingPendingFunctors_ = false;
}
这里需要注意的是,任意线程都可能会添加任务对象到这个pendingOtherThings中,所以需要用锁
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(const Functor& cb)
{
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
pendingOtherThingFunctors_.push_back(cb);
}
//如果在其他线程调用了这个函数,立即尝试唤醒handle_other_things()所在线程
if (!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_)
{
wakeup(); //写入一个字节数据到epollfd,产生可读事件,唤醒工作线程处理
}
}
总结¶
one_thread_one_loop基于Reactor模式,即主线程负责处理新来的连接,再交由工作线程处理数据;
工作线程中存在一个循环
循环中的处理:
- 监听事件(select/poll/epoll)
- 处理数据
- 做一些其他事情
存在问题:
- 主线程监听不到IO事件时,工作线程只能挂起等待,浪费时间
- 即使监听事件时设置了超时时间,工作线程也只能在未监测到IO事件前挂起,耽误了步骤三“做其他的事情”
解决问题:
- 创建
wakeup_fd,写入一个字节数据,使epollfd变为可读,做到必要时唤醒工作线程- 管道fd:
int pipefd[2]一端写入 - eventfd:
int eventfd()函数返回的句柄绑定在epollfd,一端写入 - socketpair:创建两个socket,一端写入
- 管道fd:
- 唤醒实现
- 写入一个字节数据
- 及时读取掉这一个字节数据
步骤三:处理其他事情
- 做其他事情的函数:封装一个类成员变量,使用局部变量std::vector,将类成员变量倒换进入vector,再遍历vector取出执行
- 多线程添加任务:添加其他任务到类成员变量,如果是其他线程添加任务,则唤醒“做其他事情“所在的线程(写入一个字节数据,将监测到可读事件,再”做其他事情“)